IVOA Newsletter - September 2013 (pdf)
Subscribe | Newsletter archives | Write to the editors
IVOA Newsletter Editors: Mark G. Allen, Deborah Baines, Sarah Emery Bunn,
Chenzou Cui, Mark Taylor & Ivan Zolotukhin.
The International Virtual Observatory Alliance (IVOA) was formed in June 2002 with a mission to facilitate the international coordination and collaboration necessary for the development and deployment of the tools, systems and organizational structures necessary to enable the international utilization of astronomical archives as an integrated and interoperating virtual observatory. The IVOA now comprises 20 VO programs from Argentina, Armenia, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Europe, France, Germany, Hungary, India, Italy, Japan, Russia, South Africa, Spain, Ukraine, the United Kingdom, and the United States and an inter-governmental organization (ESA). Membership is open to other national and international programs according to the IVOA Guidelines for Participation. You can read more about the IVOA and what we do at http://ivoa.net/about/.
What is the VO?
The Virtual Observatory (VO) aims to provide a research environment that will open up new possibilities for scientific research based on data discovery, efficient data access, and interoperability. The vision is of global astronomy archives connected via the VO to form a multiwavelength digital sky that can be searched, visualized, and analyzed in new and innovative ways. VO projects worldwide working toward this vision are already providing science capabilities with new tools and services. This newsletter, aimed at astronomers, highlights VO tools and technologies for doing astronomy research, recent papers, and upcoming events.
IVOA news

South Africa’s Astronomical Agreement for Big Data
The South African National Research Foundation’s three astronomical facilities have formed the South African Astroinformatics Alliance (SA3 pronounced “SA cubed”), which serves as a virtual observatory for the country. South Africa hosts new and upcoming observational facilities that will generate huge amounts of data including the Southern African Large Telescope (SALT), the Karoo Array Telescope (MeerKAT) and a large part of the SKA. See the SA3 announcement of their “Astronomical agreement signed for big data!”. SA3 is a member of the IVOA since October 2012.

News from VObs.it: Remote Telescope networks for schools: toward publishing educational data in VO
The European Hands-On-Universe Milky Way (EUHOUMW) is an educational project funded by the European Commission to bring real radio observations into classrooms, where participating students use five remotely controlled educational radio telescopes. EUHOUMW is now evaluating how to publish the collected radio data in VO format to enable data sharing (e.g. with the Italian optical robotic telescope network), to simplify data management of multi-classroom projects, and to more easily incorporate professional data in education projects. An unofficial kick-off of the collaboration between EUHOUMW and VO was held in Paris, September 5-6, 2013. The topics being addressed included; how to tag education data alongside professional data in the VO, and the use of “educationalized” VO tools (following educational use of Aladin and Stellarium). Publishing, archiving, and maintaining educational data are topics for the September 2013 IVOA Interoperability and ADASS meetings.
VO applications and implementation highlights
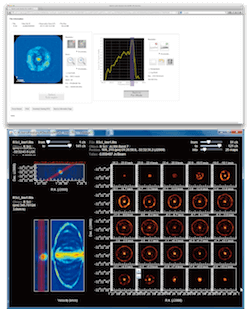
ALMA VO Service
The Japanese Virtual Observatory (JVO) and ALMA-J teams have opened a VO-based data distribution system for ALMA data cubes. The aim is to help users access public ALMA data without huge data transfers. Two user applications, ALMAWebQL and Vissage, were developed for this system. ALMAWebQL is a component of the JVO Portal and enables the user to visualize and make cut-outs of ALMA data cubes in a web browser, while Vissage is a desktop application to visualize downloaded ALMA data cubes in more detail.
More Information: http://jvo.nao.ac.jp/news/alma-vo/index.html

TheoSSA
The TheoSSA (Theoretical Stellar Spectra Access) service provides access to synthetic spectral energy distributions (SEDs) that may be calculated by any model-atmosphere code. The database contains pre-calculated SEDs over a wide range of effective temperature, surface gravity, and elemental composition. The related TMAW tool allows the calculation of individual SEDs that presently can consider opacities of the elements H, He, C, N, O, Ne, Na, and Mg.
More Information: http://dc.g-vo.org/theossa
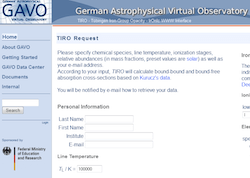
TIRO
The TIRO (Tuebingen IRon Opacity) service constructs model atoms of Ca, Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni based on Kurucz’ atomic data using a statistical approach (introducing super-levels and super-lines) and calculates the respective bound-bound and bound-free absorption cross-section.
More information: http://astro.uni-tuebingen.de/~TIRO
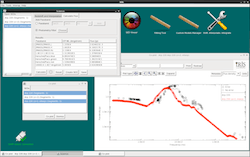
Iris version 2.0
The US VAO has released Iris 2.0, the latest version of the spectral energy distribution (SED) analysis tool. Iris comes with powerful new science capabilities which allow the redshifting, interpolation and smoothing of SEDs, and measurement of integrated fluxes through simple spectral bandpasses or through one of the thousands of photometric filters provided by the Spanish VO Filter Profile Service. Users can also apply simple aperture corrections to individual photometric points or to whole SED segments. In addition to improved visualization capabilities, including the co-plotting of SEDs, Iris 2.0 has increased interoperability with other VO tools. You can watch Iris in action in this video tutorial.
More information: http://www.usvao.org/science-tools-services/iris-sed-analysis-tool/
Some recent papers about VO-enabled science
Featured Paper
Rauch, T.; Bohlin, R.; Kruk, J. W.; Werner, K. Astronomy & Astrophysics, in press
H-rich, DA-type white dwarfs are particularly suited as primary standard stars for flux calibration. State-of-the-art NLTE models consider opacities of species up to trans-iron elements and provide reliable synthetic stellar-atmosphere spectra to compare with observation. We establish a database of theoretical spectra of stellar flux standards that are easily accessible via a web interface. In the framework of the Virtual Observatory, the German Astrophysical Virtual Observatory developed the registered service TheoSSA. It provides easy access to stellar spectral energy distributions (SEDs) and is intended to ingest SEDs calculated by any model-atmosphere code. In case of the DA white dwarf G 191-B2B, we demonstrate that the model reproduces not only its overall continuum shape but also the numerous metal lines exhibited in its ultraviolet spectrum. TheoSSA is in operation and contains presently a variety of SEDs for DA white dwarfs. It will be extended in the near future and can host SEDs of all primary and secondary flux standards. The spectral analysis of G 191-B2B has shown that our hydrostatic models reproduce the observations best at an effective temperature of 60000 +/- 2000K and a surface gravity of log g = 7.60 +/- 0.05. We newly identified Fe VI, Ni VI, and Zn IV lines. For the first time, we determined the photospheric zinc abundance with a logarithmic mass fraction of -4.89 (7.5 times solar). The abundances of He (upper limit), C, N, O, Al, Si, O, P, S, Fe, Ni, Ge, and Sn were precisely determined. Upper abundance limits of 10% solar were derived for Ti, Cr, Mn, and Co. The TheoSSA database of theoretical SEDs of stellar flux standards guarantees that the flux calibration of all astronomical data and cross-calibration between different instruments can be based on the same models and SEDs calculated with different model-atmosphere codes and are easy to compare.
Refereed Publications
-
Bayesian Analysis to Identify New Star Candidates in Nearby Young Stellar Kinematic Groups
Malo, Lison; Doyon, René; Lafrenière, David; Artigau, Étienne; Gagné, Jonathan; Baron, Frédérique; Riedel, Adric
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 762, Issue 2, article id. 88, 50 pp. (2013). -
The Pseudo-evolution of Halo Mass
Diemer, Benedikt; More, Surhud; Kravtsov, Andrey V.
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 766, Issue 1, article id. 25, 15 pp. (2013). -
Environmental Effects in the Interaction and Merging of Galaxies in zCOSMOS
Kampczyk, P. et al.
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 762, Issue 1, article id. 43, 16 pp. (2013). -
The Cosmic History of the Spin of Dark Matter Halos within the Large-scale Structure
Trowland, Holly E.; Lewis, Geraint F.; Bland-Hawthorn, Joss
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 762, Issue 2, article id. 72, 12 pp. (2013). -
Unveiling the Nature of Unidentified Gamma-Ray Sources. I. A New Method for the Association of Gamma-Ray Blazars
D’Abrusco, R.; Massaro, F.; Paggi, A.; Masetti, N.; Tosti, G.; Giroletti, M.; Smith, H. A.
The Astrophysical Journal Supplement, Volume 206, Issue 2, article id. 12, 26 pp. (2013). -
Fomalhaut b: Independent Analysis of the Hubble Space Telescope Public Archive Data
Galicher, Raphaël; Marois, Christian; Zuckerman, B.; Macintosh, Bruce
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 769, Issue 1, article id. 42, 12 pp. (2013). -
The binary fraction of planetary nebula central stars - I. A high-precision, I-band excess search
_De Marco, Orsola; Passy, Jean-Claude; Frew, D. J.; Moe, Maxwell; Jacoby, G. H.
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 428, Issue 3, p.2118-2140 -
Galaxy Zoo: bulgeless galaxies with growing black holes
Simmons, Brooke D.; Lintott, Chris; Schawinski, Kevin; Moran, Edward C.; Han, Anna; Kaviraj, Sugata; Masters, Karen L.; Urry, C. Megan; Willett, Kyle W.; Bamford, Steven P.; Nichol, Robert C.
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 429, Issue 3, p.2199-2211 -
Symbiotic stars and other Hα emission-line stars towards the Galactic bulge
Miszalski, Brent; Mikołajewska, Joanna; Udalski, Andrzej
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 432, Issue 4, p.3186-3217 -
Constraints on dark matter annihilation by radio observations of M31
Egorov, A. E.; Pierpaoli, E.
Physical Review D, vol. 88, Issue 2, id. 023504 -
Estimating gas masses and dust-to-gas ratios from optical spectroscopy
Brinchmann, Jarle; Charlot, Stéphane; Kauffmann, Guinevere; Heckman, Tim; White, Simon D. M.; Tremonti, Christy
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 432, Issue 3, p.2112-2140 -
The Detection of the Large-scale Alignment of Massive Galaxies at z ~ 0.6
Li, Cheng; Jing, Y. P.; Faltenbacher, A.; Wang, Jie
The Astrophysical Journal Letters, Volume 770, Issue 1, article id. L12, 5 pp. (2013). -
Fueling the central engine of radio galaxies. II. The footprints of AGN feedback on the ISM of 3C 236
Labiano, A.; García-Burillo, S.; Combes, F.; Usero, A.; Soria-Ruiz, R.; Tremblay, G.; Neri, R.; Fuente, A.; Morganti, R.; Oosterloo, T.
Astronomy & Astrophysics, Volume 549, id.A58, 14 pp. -
The stellar mass-size relation for the most isolated galaxies in the local Universe
Fernández Lorenzo, M.; Sulentic, J.; Verdes-Montenegro, L.; Argudo-Fernández, M.
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 434, Issue 1, p.325-335 -
The Protoplanetary Disks in the Nearby Massive Star-forming Region Cygnus OB2
Guarcello, M. G.; Drake, J. J.; Wright, N. J.; Drew, J. E.; Gutermuth, R. A.; Hora, J. L.; Naylor, T.; Aldcroft, T.; Fruscione, A.; García-Alvarez, D.; Kashyap, V. L.; King, R.
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 773, Issue 2, article id. 135, 24 pp. (2013). -
The local luminosity function of star-forming galaxies derived from the Planck Early Release Compact Source Catalogue
Negrello, M.; Clemens, M.; Gonzalez-Nuevo, J.; De Zotti, G. and 17 coauthors
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 429, Issue 2, p.1309-1323 -
A Cross-correlation Analysis of AGN and Galaxies using Virtual Observatory: Dependence on Virial Mass of Super-Massive Black Hole
Komiya, Yutaka; Shirasaki, Yuji; Ohishi, Masatoshi; Mizumoto, Yoshihiko
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 775, Issue 1, article id. 43, 12 pp. (2013).
More Ways to Find VO-related Publications
All ADS links mentioning the “virtual observatory” in the abstract
All refereed publications mentioning the “virtual observatory” in the abstract
VO calendar
-
26-28 September, 2013 - IVOA Interoperability Meeting
(Waikoloa, Hawaii, USA)
The IVOA Interop Meetings are aimed at making significant progress in defining standards and sharing best practices in the development of the world wide Virtual Observatory initiatives. The fall interop will be held just prior to the ADASS Conference (September 26-28), in the same venue. ADASS participants are welcome to attend; there is no registration fee.
-
29 Sept - 3 October 2013 - Astronomical Data Analysis Software and Systems (ADASS)
(Waikoloa, Hawaii, USA)
The ADASS conference provides a forum for scientists and programmers concerned with algorithms, software and software systems employed in the acquisition, reduction, analysis, and dissemination of astronomical data.
-
13-15 November, 2013 - Hot-wiring the Transient Universe III
(Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA)
Hot-wiring the Transient Universe 3 will explore opportunities and challenges of massively parallel time domain surveys coupled with rapid coordinated multi-wavelength follow-up observations. The interdisciplinary agenda includes future and ongoing science investigations, information infrastructure for publishing observations in real time, as well as novel data science to classify events and systems to optimize follow-up campaigns.
-
November 18, 2013 - Data-Intensive Scalable Computing Systems (DISCS-2013)
(Denver, Colorado, USA)
The primary goal of the workshop is to bring together researchers and other interested people in the areas of data intensive computing and high performance parallel computing to exchange ideas and discuss approaches for addressing the challenges facing data intensive computing at the extreme scale.
-
9-13 December, 2013 - Astroinformatics 2013: Knowledge from Data
(Sydney, Australia)
Astroinformatics is an emerging discipline at the intersection of astronomy/astrophysics and applied computer science and engineering. Registration and abstract submission for Astroinformatics 2013 are now open.
-
17-19 December 2013 - VO-Day & Friends
(Catania, Italy)
This workshop, organized by VObs.it and IA2, on behalf of the EURO-VO project, will be a 3-day meeting for the Italian community focusing on VO dissemination and tutorials, the connections of VO with grid/cloud/HPC, and hands-on work on science gateways.
-
7 January 2014 - Building the Astronomical Information Sciences: From NASA’s AISR Program to the New AAS Working Group on Astroinformatics and Astrostatistics
This special session at the 223rd AAS meeting will showcase science results that were at least partially enabled by modern astroinformatics and astrostatistics tools. There will also be a poster session associated with this Special Session. Abstracts are being accepted via the regular AAS form and are due October 1, 2013.
-
17-20 June, 2014 - LISA (Library and Information Services in Astronomy VII)
(Naples, Italy)
