IVOA NEWSLETTER - October 2011 (pdf)
The International Virtual Observatory Alliance (IVOA) was formed in June 2002 with a mission to facilitate the international coordination and collaboration necessary for the development and deployment of the tools, systems and organizational structures necessary to enable the international utilization of astronomical archives as an integrated and interoperating virtual observatory. The IVOA now comprises 19 VO programs from Argentina, Armenia, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Europe, France, Germany, Hungary, India, Italy, Japan, Russia, Spain, the United Kingdom, and the United States and inter-governmental organizations (ESA and ESO). Membership is open to other national and international programs according to the IVOA Guidelines for Participation. You can read more about the IVOA and what we do at http://www.ivoa.net/pub/info/.
What is the VO?
The Virtual Observatory (VO) aims to provide a research environment that will open up new possibilities for scientific research based on data discovery, efficient data access, and interoperability. The vision is of global astronomy archives connected via the VO to form a multiwavelength digital sky that can be searched, visualized, and analyzed in new and innovative ways. VO projects worldwide working toward this vision are already providing science capabilities with new tools and services. This newsletter, aimed at astronomers, highlights VO tools and technologies for doing astronomy research, recent papers, and upcoming events.
IVOA news

IVOA Recommendations Available from arXiv & ADS
All the core IVOA documents are now available from arXiv and are listed in ADS. This currently includes all IVOA Recommendations as well as the IVOA Architecture paper. This gives the documents greater exposure and provides a simple, standard way for people to cite these important publications in the mainstream literature. All IVOA recommendations currently in ADS can be found here. We plan to update the list in the near future and incorporate all these papers in the main astronomy database.
VO applications highlights

US VAO’s Iris SED Analysis Tool
Iris is a new desktop tool for construction and analysis of spectral energy distributions (SEDs). Iris enables the construction of an SED from multiple spectral and photometric data segments across a wide spectral range. It also allows the user to fit the resulting SED with empirical and/or theoretical models. SED data may be uploaded into the application from VOTable and FITS format files, or imported directly from the NASA Extragalactic Database (NED). Iris also includes the capability to convert from other formats to a FITS or VOTable. Iris also writes the resulting SEDs, and their fits, to external data files.
More Information: http://www.usvao.org/tools/
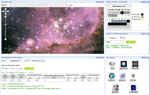
VOIPortal
VOIPortal is an entry point to all VO-India (VOI) web services including the VOI Mosaic and PyMorph web applications. Users can also browse & download data produced by Mosaic and PyMorph in their VOI userspace. The beta release of VOIPortal includes enhancements such as the ability to add iGoogle gadgets, sharing gadgets, support for multiple tabs, and ‘drag and drop’ layout changes. VOI gadgets are also published to the iGoogle gadget directory.
More information: http://vo.iucaa.ernet.in/~voi/VOIPortal.html
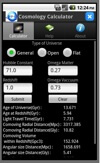
VO-India Android application
VO-India releases Android Cosmological Calculator v1.0 Beta. Given user input values for the Hubble constant, Omega(matter), Omega(vacuum) and redshift, the Cosmological Calculator returns the co-moving radial distance and volume, the angular-size distance at the specified redshift, the scale (kpc/arcsec), and the luminosity distance. One may also choose between a flat and open universe. This application is published as a free downloadable *.apk file and can be installed on any Android 2.2 or higher mobile device. The Cosmological Calculator has been adapted from Ned Wright’s Cosmology Calculator.
More information: http://vo.iucaa.ernet.in/~voi/voandroidcc.htm
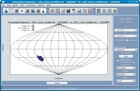
VOPlot v1.7
In v1.6, VOPlot had undergone a major GUI upgrade making it simpler and more flexible to use. All the plots are dynamically linked to each other as well as to the launcher. The user can now plot columns from different VOTables against each other. VOPlot v1.7 builds on this and has a host of new features, including a classic “outline” format for 2D histogram, additional functionality for projection plots (e.g. support for Galactic Lat/Long), cone search with multi-word searching, and the use of the logical operators AND/OR. VOPlot v1.7 also provides better handling of “faulty data” while parsing an ascii file. All this comes with a fully updated user guide as well.
More information: http://vo.iucaa.ernet.in/~voi/voplot.htm
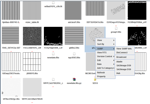
FITSManager
FITSManager is a desktop application for astronomers to efficiently manage and use FITS files hosted in their personal computers, bringing the VO to its users in a seamless and transparent way. FITSManager provides specific functions for FITS file management like thumbnail, preview, type dependent icons, and header keyword indexing and search. FITSManager supports SAMP, so that files in FITS or VOTable can be sent to SAMP-ready VO tools such as Aladin or TOPCAT. (Published paper)
More information: http://fm.china-vo.org
Some recent papers about VO-enabled science
Featured Paper
Astroinformatics of galaxies and quasars: a new general method for photometric redshifts estimation
Laurino, O.; D’Abrusco, R.; Longo, G.; Riccio, G.
With the availability of the huge amounts of data produced by current and future large multi-band photometric surveys, photometric redshifts have become a crucial tool for extragalactic astronomy and cosmology. In this paper we present a novel method, called Weak Gated Experts (WGE), which allows to derive photometric redshifts through a combination of data mining techniques. The WGE, like many other machine learning techniques, is based on the exploitation of a spectroscopic knowledge base composed by sources for which a spectroscopic value of the redshift is available. This method achieves a variance in the redshift residuals (zphot - zspec) of 2.3x10-4 and 0.08 for the reconstruction of the photometric redshifts for the optical galaxies from the SDSS and for the optical quasars respectively, while the Root Mean Square (RMS) of the redshift residuals distributions for the two experiments is respectively equal to 0.021 and 0.35. The WGE provides also a mechanism for the estimation of the accuracy of each photometric redshift. We also present and discuss the catalogs obtained for the optical SDSS galaxies, for the optical candidate quasars extracted from the DR7 SDSS photometric dataset, and for optical SDSS candidate quasars observed by GALEX in the UV range. The WGE method exploits the new technological paradigm provided by the Virtual Observatory and the emerging field of Astroinformatics.
2011 Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, in press
Refereed Publications
- WISE/2MASS-SDSS brown dwarfs candidates using Virtual Observatory tools
Aberasturi, M., Solano, E., Martin, E. L.
2011 Astronomy & Astrophysics, in press - A universal ultraviolet-optical colour-colour-magnitude relation of galaxies
Chilingarian, Igor; Zolotukhin, Ivan
2011 Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, in press - TESELA: a new Virtual Observatory tool to determine blank fields for astronomical observations
Cardiel, N.; Jiménez-Esteban, F. M.; Alacid, J. M.; Solano, E.; Aberasturi, M.
2011 Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Online Early - Defining and cataloging exoplanets: the exoplanet.eu database
Schneider, J.; Dedieu, C.; Le Sidaner, P.; Savalle, R.; Zolotukhin, I.
2011 Astronomy & Astrophysics, Volume 532, id.A79 - Estimation of the XUV radiation onto close planets and their evaporation
Sanz-Forcada, J., Micela, G., Ribas, I., Pollock, A. M. T., Eiroa, C., Velasco, A., Solano, E., Garcia-Alvarez, D.
2011 Astronomy & Astrophysics, 532, A6 - On the use of the Virtual Observatory to select calibrators for phase-referenced astrometry of exoplanet-host stars
Beust H., Bonneau D., Mourard D., Lafrasse S., Mella G., Duvert G., Chelli A.
2011 Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 414, Issue 1, pp. 108-115 - A search for new hot subdwarf stars by means of Virtual Observatory tools
Oreiro R., Rodriguez-Lopez C., Solano E., Ulla A., Ostensen R., Garcia-Torres M
Astronomy & Astrophysics, Volume 530, id.A2 - New Optical Reddening Maps of the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds
Haschke R., Grebel E.K., Duffau S.
2011 The Astronomical Journal, Volume 141, Issue 5, article id. 158 - Early Science Result from the Japanese Virtual Observatory: AGN and Galaxy Clustering at z = 0.3 to 3.0Y.
Shirasaki, M. Tanaka, M. Ohishi, Y. Mizumoto, N. Yasuda, and T. Taka.
2011 Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan, Vol.63, No.SP2, pp.469–491 - Enhanced Management of Personal Astronomical Data with FITSManager
Chenzhou Cui, Dongwei Fan, Yongheng Zhao, Ajit Kembhavi, Boliang He, Zihuang Cao, Jian Li, Deoyani Nandrekar
2011 Accepted for publication in New Astronomy - Photometric Catalogue of Quasars and Other Point Sources in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey
Sheelu Abraham, Ninan Sajeeth Philip, Ajit Kembhavi, Yogesh G Wadadekar, Rita Sinha
2011 Accepted for publication in MNRAS Main Journal
More Ways to Find VO-related Publications
- All ADS links mentioning the “virtual observatory” in the abstract
- All refereed publications mentioning the “virtual observatory” in the abstract
VO calendar
-
10-13 October, 2011 - National Workshop on Science with the Virtual Observatory
(Kochi, India)
With newer tools for the acquisition and processing of astronomical data from archives being introduced by the worldwide VO community, research in astronomy has become easier than ever before. Newman Collage, (Kerala, India) in collaboration with IUCAA (Pune, India) is conducting a national workshop on Science with the Virtual Observatory to present the latest developments in the VO to the research community.
-
17-21 October, 2011 - IVOA Interoperability Meeting
(Pune, India)
The IVOA Interop Meetings are aimed at making significant progress in defining standards and sharing best practices in the development of the world wide Virtual Observatory initiatives.
-
8 January, 2012 - “Science Tools for Data-Intensive Astronomy” VO Workshop at AAS 219
(Austin, TX)
This workshop will be focused on the science tools for data discovery, visualization, and analysis. The workshop is structured in the form of two independent half-day sessions (the first half aimed at high school and community college educators, the second at research astronomers) and is designed to demonstrate the emerging set of tools and services for data-intensive astronomy. To register for an AAS workshop, please visit the conference website. In cases of documented need, the $35 registration fee can be reimbursed upon request. Organized and sponsored by the US Virtual Astronomical Observatory.
-
May 2012 - IVOA Interoperability Meeting
(Washington, DC) (To Be Confirmed)
The IVOA Interop Meetings are aimed at making significant progress in defining standards and sharing best practices in the development of the world wide Virtual Observatory initiatives.
IVOA Newsletter Editors:
- Mark G. Allen
- Sarah Emery Bunn
- Chenzou Cui
- Evanthia Hatziminaoglou
- Thomas. A. McGlynn
- Christopher J. Miller
- Jonathan Tedds
